Hypoglycemia in neonates refers to low blood sugar levels in newborns, which can result in serious health issues if unnoticed and untreated. This condition occurs when a newborn’s glucose level falls below the normal range, crucial for energy supply to vital organs. The brain needs a constant supply of glucose immediately after birth when newborns are highly dependent on it.
Glucose is the brain’s main source of energy, crucial for development and function. It powers activities involved in thinking, motor skills, and senses, making adequate glucose levels vital. Without enough glucose in newborns, brain function might suffer, potentially affecting development if ignored for too long.
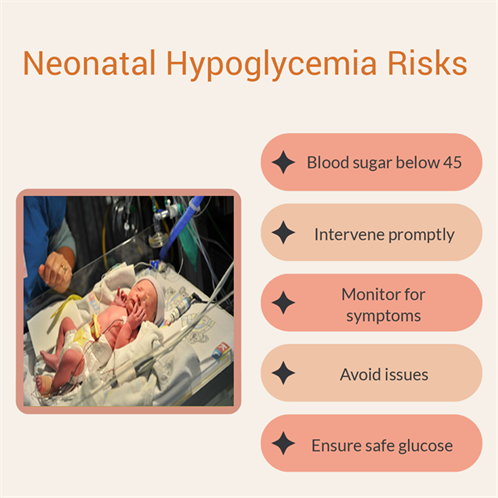
Knowing the signs of hypoglycemia in newborns early can prevent severe issues. Parents have a crucial role by keeping an eye on their baby’s health. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking medical help promptly can protect a newborn from complications linked with ongoing hypoglycemia.
Knowing Hypoglycemia in Newborns
Hypoglycemia in a neonate means when a newborn’s sugar level drops too low. The range considered safe is above 45 mg/dL for infants, and knowing the right limit ensures timely treatment. Correct levels prevent any complications from arising early on in a newborn’s life.
Glucose is an important energy source for babies’ cells and brains, aiding their quick growth. It gets stored in their liver as glycogen to use when needed. This provides energy, especially when they no longer receive glucose from the mother.
Babies face drastic changes after birth that can lower glucose levels significantly. Once born, they lose the direct sugar supply from the mother, relying on breast milk or formula instead. Factors like the mother’s health, baby’s birth weight, and gestation period affect how effectively a newborn handles these changes and maintains normal levels.
Identifying Causes of Hypoglycemia in Neonates
Newborns can have low blood sugar due to limited energy reserves. This is common in preterm infants or those small at birth. Their ability to keep normal blood sugar is reduced due to these factors.
In some newborns, high insulin levels can cause blood sugar problems. It results from the pancreas releasing too much insulin, using up available glucose quickly. Cases like these may also be linked to hormone issues or effects of maternal medication.
Maternal health plays a crucial role in neonatal glucose levels, with existing medical conditions such as diabetes impacting outcomes. Stress or poor nutrition during pregnancy also raises newborn hypoglycemia risks, making monitoring essential.
Early Symptoms of Hypoglycemia: Recognize the Signs
The initial signs of hypoglycemia in neonate might be subtle and easily missed. These symptoms may appear gradually, blending with normal newborn behaviors, making it hard to spot.
Notable symptoms of newborn hypoglycemia include shakiness, poor feeding, and low energy levels. Infants may also show irritability and increased crying from instability in glucose levels for newborns. Caregivers need sharp eyes to notice these signs among typical behaviors.
Serious symptoms can include lethargy, seizures, or even loss of consciousness. These indicate severe hypoglycemia in newborn infants and require urgent medical help to prevent long-term harm.
Diagnosing Hypoglycemia in Newborns
Diagnosis involves bedside glucose checks, showing the infant’s blood sugar levels quickly. These simple tests are essential, so care can be adjusted quickly. Often, they provide results to decide if feeding or intravenous glucose is needed.
Screening early is vital for babies at risk, like those from diabetic mothers or premature births. By checking early, doctors can spot and address low blood sugar in newborns before it leads to problems.
If a newborn’s low blood sugar continues, detailed tests might be used for a true assessment. In cases of persistent hypoglycemia in newborns, doctors might check hormones like cortisol and growth hormone to find any underlying issues.
Effective Solutions and Treatments for Newborn Hypoglycemia
Feeding the baby quickly can help raise their blood sugar levels. Breastfeeding or using a bottle works well to get things normal.
Sometimes, the baby might need more help in the hospital. They might give IV glucose if regular feedings aren’t enough. Special care might be needed for serious cases in the hospital.
After this, it’s important to watch the baby’s blood sugar often. Parents learn how to spot signs and make sure feedings keep the sugar right. Keeping up with these steps can stop low sugar problems later.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Hypoglycemia Risks
Managing your health during pregnancy reduces hypoglycemia risk in neonates. Keeping an eye on glucose levels helps spot any potential issues early. Balanced meals plus staying active can make a big difference. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are very important.
Hospitals must test blood sugar of newborns right after birth for clear reasons. If there are risks, early tests help catch problems fast. Newborn screenings help prevent serious complications by ensuring proper interventions.
Parents should know the signs of low blood sugar in newborn infants. Keep an eye out for signs like poor feeding or irritability. Quick feeding and seeking medical help when unsure is essential. Consult the medical team to keep sugar levels stable.
Decoding When to Seek Medical Help
Parents should observe any unusual signs in their babies, like jitteriness or seizures. If your baby is excessively drowsy, this might signal a blood sugar issue. Always trust your instincts as a parent when something feels off.
Once at the healthcare facility, staff will check the baby’s blood sugar levels. Doctors will assess symptoms and decide on necessary treatments. You can expect them to act quickly for the best recovery chance.
Most newborns recover well with fast medical action for low blood sugar. Prompt medical care significantly improves outcomes, and staff prioritize returning glucose levels to normal.
Exploring Long-term Implications of Untreated Hypoglycemia
Ignoring signs of hypoglycemia in a newborn can lead to complications. Problems like developmental delays often occur if left unattended.
Acting quickly is essential to avoid long-term issues and harm. Correct management prevents brain damage, ensuring healthy growth and development.
Parents should watch their child’s blood glucose levels carefully. Regular check-ups and consulting doctors help maintain proper glucose levels.
Conclusion: Why Awareness Can Save Lives
Early identification of neonatal hypoglycemia symptoms is vital for proper care.
Parents are primarily responsible for monitoring a newborn’s health closely. They can detect signs of low blood sugar faster than anyone else.
Through education about newborn blood glucose, parents feel more prepared. Learning about glucose levels empowers proactive management against potential complications.
Worried About Your Newborn’s Sugar Levels?
At Dr. Preeti Maternity Centre, we ensure early detection and expert care for neonatal hypoglycemia.
Your baby’s health starts with timely attention.
Schedule a newborn check-up today—because every heartbeat deserves a healthy start.